In the bustling world of digital marketing, businesses often grapple with choosing between paid advertising and organic marketing to boost their online presence. Let’s break down these concepts, explore real-life examples, and analyze which strategy might work best for your business.
Understanding the Basics
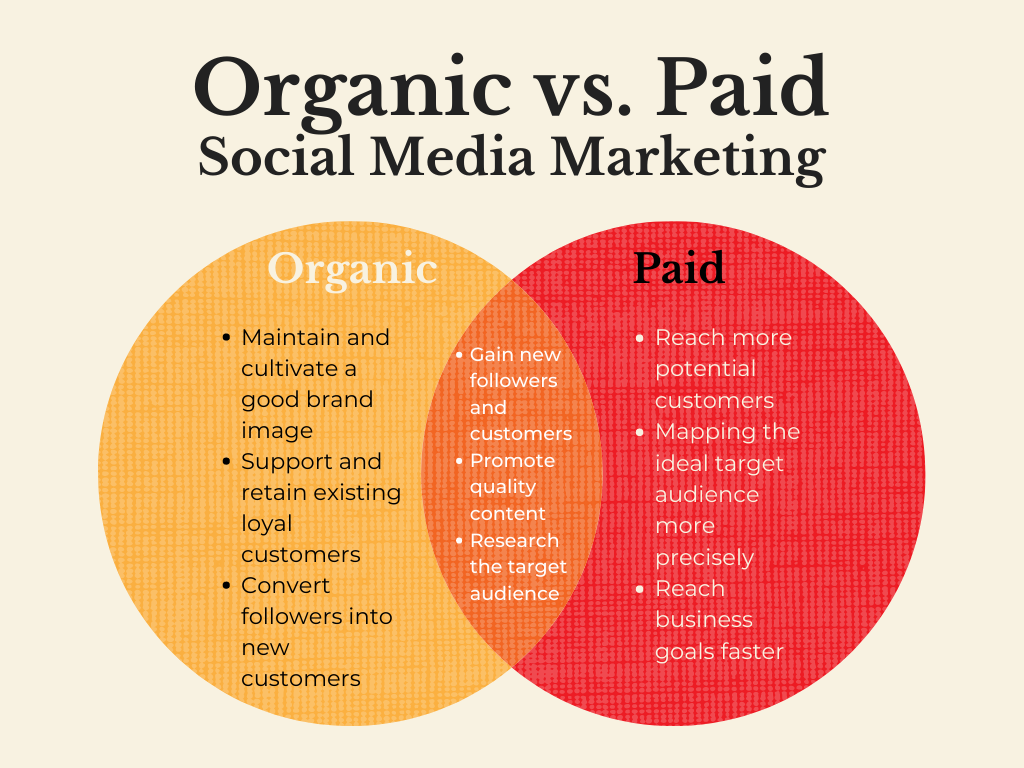
Paid Advertising involves businesses paying to promote their products or services. This includes methods like pay-per-click (PPC) ads, display ads, and sponsored posts. Essentially, companies spend money to get their message in front of potential customers.
Organic Marketing, on the other hand, focuses on naturally attracting customers without direct payment for advertising space. This strategy encompasses search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, and social media engagement. The goal is to build a loyal audience over time through valuable and relevant content.
Simplifying the Concepts
Imagine you have a lemonade stand. If you pay someone to shout, “Buy this lemonade!” to passersby, that’s like paid advertising—you’re spending money to get immediate attention. If you instead set up a colorful stand, offer free samples, and let people talk about how tasty your lemonade is, that’s like organic marketing—you’re attracting customers naturally by creating something they value and want to share.
Real-Life Examples
Paid Advertising: During major events like the Super Bowl, companies invest millions in commercials to capture the attention of a vast audience. For instance, in 2024, brands spent up to $8 million for a 30-second Super Bowl ad, aiming for immediate visibility and brand recognition.
Organic Marketing: Luxury fashion brands are increasingly leveraging employee-generated content to promote authenticity and engage audiences. Employees from different levels, including creative directors and craftsmen, share behind-the-scenes insights, creating relatable content that resonates with consumers without direct advertising costs.
Pros and Cons
Paid Advertising:
Pros: Immediate results, targeted reach, and measurable outcomes.
Cons: Can be costly, short-term impact, and potential ad fatigue among consumers.
Organic Marketing:
Pros: Cost-effective, builds trust over time, and offers lasting results.
Cons: Requires time and consistent effort, with slower initial results.
What Do the Numbers Say?
Cost: Organic marketing is typically less expensive than paid marketing. As long as you have an understanding of SEO, you can optimize your website and other content for organic search with very little budget.
Longevity: While paid ads can drive traffic quickly, the results often don’t last long. Unlike organic methods, which can create long-term value, the benefits of paid traffic only last as long as you keep paying for it.
Which Strategy Works Best?
The optimal approach depends on your business goals:
For Immediate Visibility: If you’re launching a new product or aiming for quick engagement, paid advertising can provide rapid results.
For Sustainable Growth: If you’re focused on building a loyal customer base and long-term brand recognition, organic marketing is the way to go.
Many successful businesses integrate both strategies, using paid ads for immediate boosts while investing in organic methods for sustained growth.
Conclusion
Balancing paid advertising and organic marketing is crucial for a well-rounded digital strategy. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each, you can tailor your approach to align with your business objectives and resources.
Remember, in the digital marketing landscape, it’s not about choosing one over the other but finding the right mix that propels your business forward.
